Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Radiation Research, 163(2), p.241 - 246, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:64.73(Biology)As the first step for the analysis of the biological effect of heavy charged-particle radiation, we established a method for the irradiation of individual cells with a heavy ion microbeam apparatus at JAERI-Takasaki. CHO-K1 cells attached on the thin film of ion track detector, CR-39, were automatically detected under fluorescent microscope, and irradiated individually with  Ar
Ar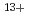 ion (11.5 MeV/u, LET=1260 keV/
ion (11.5 MeV/u, LET=1260 keV/ m) microbeam. Without killing the irradiated cells, trajectories of irradiated ions were visualized as etch-pits by treatment of CR-39 with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37
m) microbeam. Without killing the irradiated cells, trajectories of irradiated ions were visualized as etch-pits by treatment of CR-39 with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37 C. The exact positions of ion hits were determined by overlaying images of both cells and etch-pits. The cells that were irradiated with argon ions showed a reduced growth in post-irradiate observations. Moreover, a single hit of an argon ion to the cell nucleus resulted in strong growth inhibition. These results tell us that our truthful irradiation method now enables us to start a precise study of the cellular response of high-LET radiation effects on cells.
C. The exact positions of ion hits were determined by overlaying images of both cells and etch-pits. The cells that were irradiated with argon ions showed a reduced growth in post-irradiate observations. Moreover, a single hit of an argon ion to the cell nucleus resulted in strong growth inhibition. These results tell us that our truthful irradiation method now enables us to start a precise study of the cellular response of high-LET radiation effects on cells.
Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Radiation Research, 161(1), p.111 - 112, 2004/01
Using the heavy ion microbeam apparatus, mammalian cells were irradiated in the atmosphere with a single or precise numbers of  Ar heavy ions (11.5 MeV/u) with a spatial resolution of a few microns. Positional data of the individual cells attached on the ion track detector CR-39 were obtained at the off-line microscope before irradiation, then the targeting and irradiation of the cells were performed semi-automatically at the on-line microscope of the microbeam apparatus according to the obtained data. Immediately after irradiation, the position and the number of ion tracks traversed the cell was detected with etching of CR-39 at 37
Ar heavy ions (11.5 MeV/u) with a spatial resolution of a few microns. Positional data of the individual cells attached on the ion track detector CR-39 were obtained at the off-line microscope before irradiation, then the targeting and irradiation of the cells were performed semi-automatically at the on-line microscope of the microbeam apparatus according to the obtained data. Immediately after irradiation, the position and the number of ion tracks traversed the cell was detected with etching of CR-39 at 37  C. The growths of the cells were observed individually up to 60 hours after irradiation. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that single Ar ion traversal of cell nucleolus resulted to complete growth inhibition of the irradiated cells.
C. The growths of the cells were observed individually up to 60 hours after irradiation. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that single Ar ion traversal of cell nucleolus resulted to complete growth inhibition of the irradiated cells.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210(1-4), p.308 - 311, 2003/09
A method for detecting the ion hit tracks on the mammalian cultured cells at the irradiation time was established. The cells were attached to the ion track detector CR-39 (100  m thick), then irradiated with 13.0 MeV/u 20Ne or 11.5 MeV/u 40Ar ion beams. Immediately after the irradiation, the cells were refilled with medium, then the CR-39 was etched from the opposite side of the cell with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37
m thick), then irradiated with 13.0 MeV/u 20Ne or 11.5 MeV/u 40Ar ion beams. Immediately after the irradiation, the cells were refilled with medium, then the CR-39 was etched from the opposite side of the cell with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37 C. With the 15 min etching treatment, we obtained the accurate information about the spatial distribution of irradiated ions without significant effect on the cell growth. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that the growth of ion hit cell was reduced compared with that of non-irradiated one.
C. With the 15 min etching treatment, we obtained the accurate information about the spatial distribution of irradiated ions without significant effect on the cell growth. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that the growth of ion hit cell was reduced compared with that of non-irradiated one.
Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Hoshasen Seibutsu Kenkyu, 37(3), p.334 - 347, 2002/09
In JAERI-Takasaki, the heavy ion microbeam system was developed, and utilized to irradiate biological materials. However, the utilization of microbeam system was mainly in the radio-surgery tool for analyzing insect development and plant root differentiation. This was because some beam technological and biological difficulties existed in irradiating cultured cell with high LET ion beam. Recently, we established a efficient and practical way for irradiating mammalian cultured cell with our microbeam apparatus. In this paper, the outlines of our micro beam system and the actual process for cultured cell irradiation will be described.